4.4. Coordinate Systems and TF Transforms
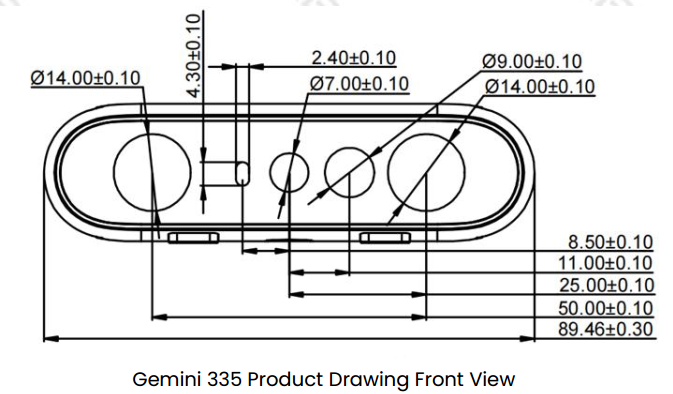
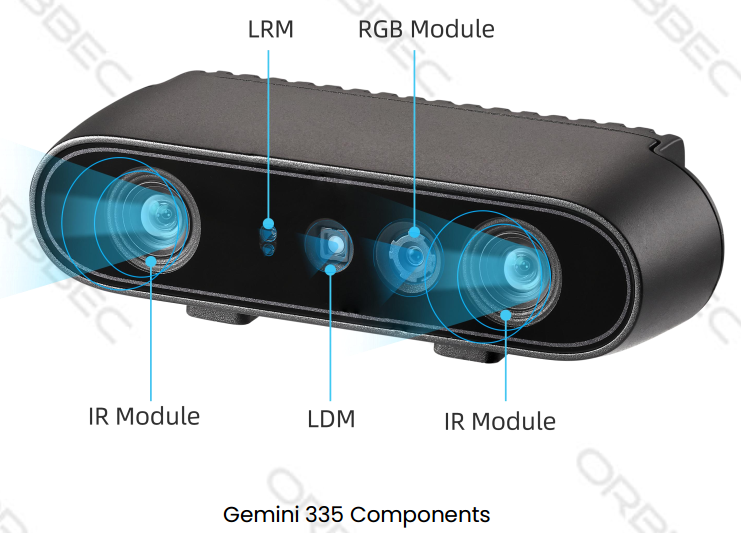
4.4.1. Camera sensor structure
4.4.2. ROS Robot Coordinate System vs Camera Optical Coordinate System
Observation perspective:
Imagine we stand behind the camera looking forward.
Always use this perspective when discussing coordinates, left/right IR, sensor positions, etc.
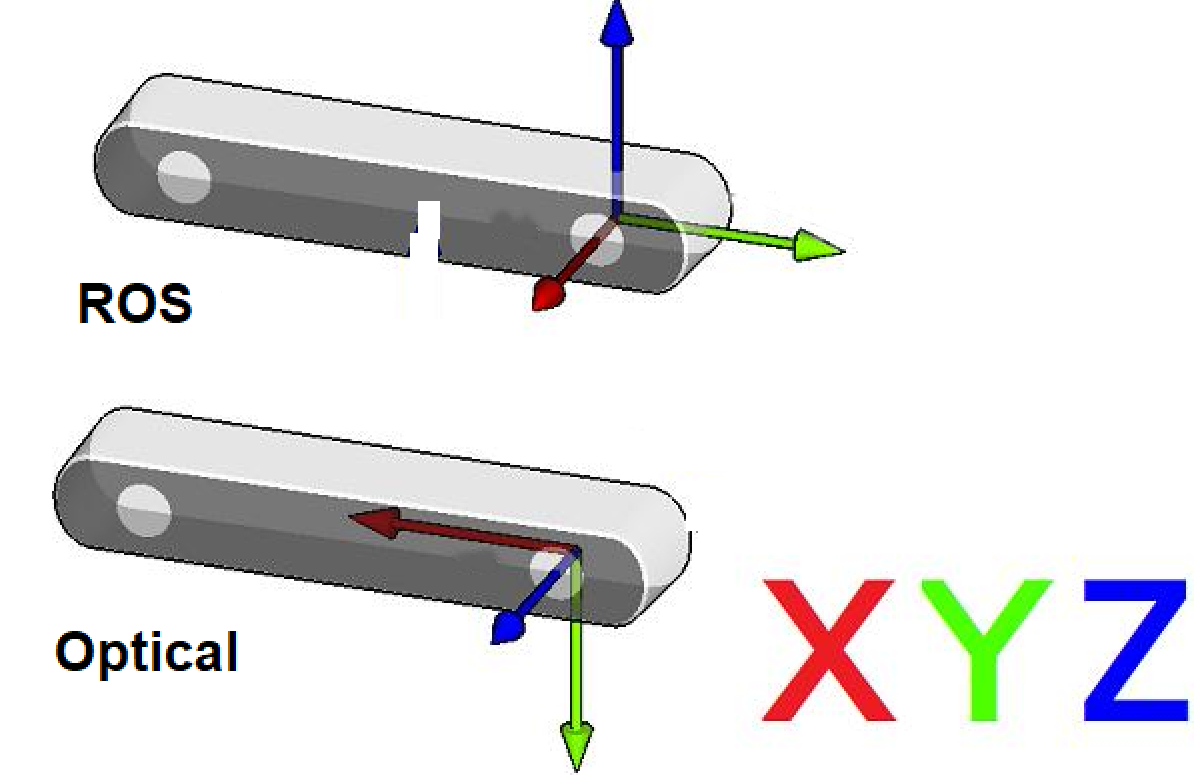
ROS coordinate system: (X: forward, Y: left, Z: up)
Camera optical coordinate system: (X: right, Y: down, Z: forward)
All data published by the wrapper topics are directly from the camera sensors in the optical coordinate system.
Static and dynamic TF topics publish both the optical and ROS coordinate systems, giving users the ability to transform between them.
4.4.3. Using ROS1 TF Tools
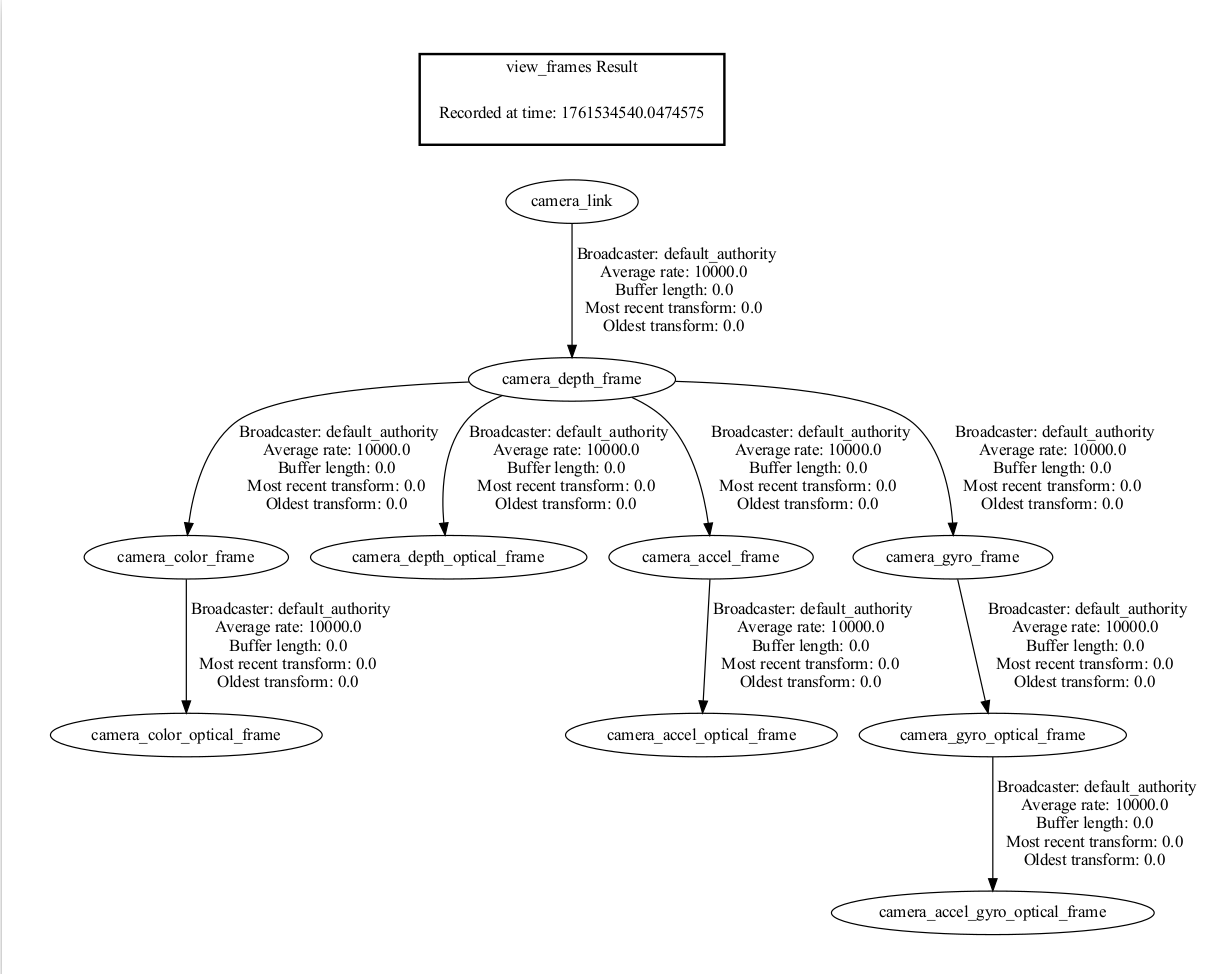
4.4.3.1. View TF Tree Structure
You can use the following ROS1 commands to print and visualize the TF tree published by the camera package:
Print all TF relationships:
rosrun tf view_frames
This command generates a frames.pdf file that shows the hierarchical relationships between all frames.
View all currently published TF information:
rostopic echo /tf_static
View the TF transform between two specified frames:
Use the following command to view the transform between two specific frames:
rosrun tf tf_echo [source_frame] [target_frame]
For example, to view the transform from camera_link to camera_depth_optical_frame:
rosrun tf tf_echo camera_link camera_depth_optical_frame
This command continuously outputs the real-time transform information between the two frames, including:
Translation: x, y, z
Rotation: Quaternion (x, y, z, w) and Euler angles (roll, pitch, yaw)
Sample output:
At time 0.000
- Translation: [0.000, 0.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [-0.500, 0.500, -0.500, 0.500]
in RPY (radian) [-1.571, -0.000, -1.571]
in RPY (degree) [-90.000, -0.000, -90.000]
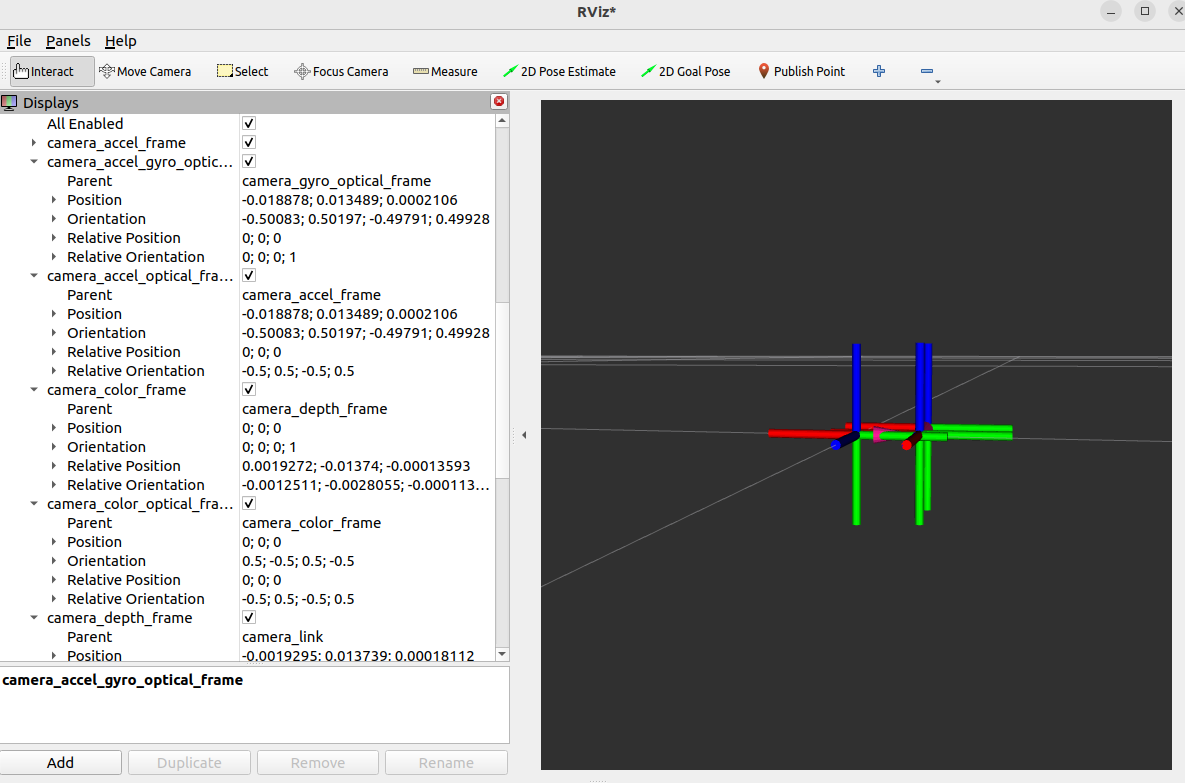
4.4.3.2. Visualize the TF Tree in rviz
You can visualize the TF tree structure and relative frame positions in real time in rviz:
rviz
In rviz:
Add the
TFdisplay pluginSet the Fixed Frame to
camera_linkorcamera_depth_optical_frame, etc.Select the TF frames to display
4.4.4. ROS1 Camera TF Calculation and Publication Mechanism
4.4.4.1. Core Function: OBCameraNode::calcAndPublishStaticTransform()
The camera node uses this function to compute and publish all static transforms between sensors.
void OBCameraNode::calcAndPublishStaticTransform() {
tf2::Quaternion quaternion_optical, zero_rot;
zero_rot.setRPY(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
quaternion_optical.setRPY(-M_PI / 2, 0.0, -M_PI / 2);
tf2::Vector3 zero_trans(0, 0, 0);
if (!stream_profile_.count(base_stream_)) {
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Base stream is not available");
return;
}
auto base_stream_profile = stream_profile_[base_stream_];
CHECK_NOTNULL(base_stream_profile.get());
for (const auto& item : stream_profile_) {
auto stream_index = item.first;
auto stream_profile = item.second;
if (!stream_profile) {
continue;
}
OBExtrinsic ex;
try {
ex = stream_profile->getExtrinsicTo(base_stream_profile);
} catch (const ob::Error& e) {
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Failed to get " << stream_name_[stream_index]
<< " extrinsic: " << e.getMessage());
ex = OBExtrinsic({{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0}});
}
auto Q = rotationMatrixToQuaternion(ex.rot);
Q = quaternion_optical * Q * quaternion_optical.inverse();
Q = Q.normalize();
tf2::Vector3 trans(ex.trans[0], ex.trans[1], ex.trans[2]);
auto timestamp = ros::Time::now();
if (stream_index.first != base_stream_.first) {
if (stream_index.first == OB_STREAM_IR_RIGHT && base_stream_.first == OB_STREAM_DEPTH) {
trans[0] = std::abs(trans[0]); // because left and right ir calibration is error
}
publishStaticTF(timestamp, trans, Q, frame_id_[base_stream_], frame_id_[stream_index]);
}
publishStaticTF(timestamp, zero_trans, quaternion_optical, frame_id_[stream_index],
optical_frame_id_[stream_index]);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Publishing static transform from " << stream_name_[stream_index] << " to "
<< stream_name_[base_stream_]);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Translation " << trans[0] << ", " << trans[1] << ", " << trans[2]);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Rotation " << Q.getX() << ", " << Q.getY() << ", " << Q.getZ() << ", "
<< Q.getW());
}
auto device_info = device_->getDeviceInfo();
CHECK_NOTNULL(device_info);
auto pid = device_info->pid();
if ((pid == FEMTO_BOLT_PID || pid == FEMTO_MEGA_PID) && enable_stream_[DEPTH] &&
enable_stream_[COLOR]) {
// calc depth to color
CHECK_NOTNULL(stream_profile_[COLOR]);
auto depth_to_color_extrinsics = base_stream_profile->getExtrinsicTo(stream_profile_[COLOR]);
auto Q = rotationMatrixToQuaternion(depth_to_color_extrinsics.rot);
Q = quaternion_optical * Q * quaternion_optical.inverse();
Q = Q.normalize();
publishStaticTF(ros::Time::now(), zero_trans, Q, camera_link_frame_id_,
frame_id_[base_stream_]);
} else {
publishStaticTF(ros::Time::now(), zero_trans, zero_rot, camera_link_frame_id_,
frame_id_[base_stream_]);
}
}
4.4.4.2. Function Explanation
Below is a detailed explanation of the ROS1 code:
Quaternion Initialization and Coordinate System Transformation
tf2::Quaternion quaternion_optical, zero_rot;
zero_rot.setRPY(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
quaternion_optical.setRPY(-M_PI / 2, 0.0, -M_PI / 2);
tf2::Vector3 zero_trans(0, 0, 0);
quaternion_optical: Defines the rotation transforming the camera optical coordinate system to the ROS standard coordinate system (90-degree rotations). This rotates from camera optical (X right, Y down, Z forward) to ROS standard (X forward, Y left, Z up).zero_trans: Used for publishing transforms that only include rotation.
Base Stream
auto base_stream_profile = stream_profile_[base_stream_];
CHECK_NOTNULL(base_stream_profile.get());
Select a base stream (usually depth). All other sensor transforms are computed relative to this base stream.
Iterate Over All Streams and Compute Relative Transforms
for (const auto& item : stream_profile_) {
auto stream_index = item.first;
auto stream_profile = item.second;
if (!stream_profile) {
continue;
}
OBExtrinsic ex;
try {
ex = stream_profile->getExtrinsicTo(base_stream_profile);
} catch (const ob::Error& e) {
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Failed to get " << stream_name_[stream_index]
<< " extrinsic: " << e.getMessage());
ex = OBExtrinsic({{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0}});
}
auto Q = rotationMatrixToQuaternion(ex.rot);
Q = quaternion_optical * Q * quaternion_optical.inverse();
Q = Q.normalize();
tf2::Vector3 trans(ex.trans[0], ex.trans[1], ex.trans[2]);
auto timestamp = ros::Time::now();
This transform converts the camera’s native optical coordinate system into the ROS standard coordinate system.
Publish TF Transforms
if (stream_index.first != base_stream_.first) {
if (stream_index.first == OB_STREAM_IR_RIGHT && base_stream_.first == OB_STREAM_DEPTH) {
trans[0] = std::abs(trans[0]); // because left and right ir calibration is error
}
publishStaticTF(timestamp, trans, Q, frame_id_[base_stream_], frame_id_[stream_index]);
}
publishStaticTF(timestamp, zero_trans, quaternion_optical, frame_id_[stream_index],
optical_frame_id_[stream_index]);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Publishing static transform from " << stream_name_[stream_index] << " to "
<< stream_name_[base_stream_]);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Translation " << trans[0] << ", " << trans[1] << ", " << trans[2]);
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Rotation " << Q.getX() << ", " << Q.getY() << ", " << Q.getZ() << ", "
<< Q.getW());
First
publishStaticTF: Published only when the current stream is not the base stream. Contains translation + rotation from base stream to current sensor.Second
publishStaticTF: Publishes the transform from the physical frame to the optical frame (pure rotation, no translation).frame_id_[stream_index]: Physical frame name (e.g.,camera_depth_frame).optical_frame_id_[stream_index]: Optical frame name (e.g.,camera_depth_optical_frame).Special handling for left/right IR camera X-axis offset using
abs()to ensure positive value.
Special Device Handling (FEMTO Series)
auto device_info = device_->getDeviceInfo();
CHECK_NOTNULL(device_info);
auto pid = device_info->pid();
if ((pid == FEMTO_BOLT_PID || pid == FEMTO_MEGA_PID) && enable_stream_[DEPTH] &&
enable_stream_[COLOR]) {
// calc depth to color
CHECK_NOTNULL(stream_profile_[COLOR]);
auto depth_to_color_extrinsics = base_stream_profile->getExtrinsicTo(stream_profile_[COLOR]);
auto Q = rotationMatrixToQuaternion(depth_to_color_extrinsics.rot);
Q = quaternion_optical * Q * quaternion_optical.inverse();
Q = Q.normalize();
publishStaticTF(ros::Time::now(), zero_trans, Q, camera_link_frame_id_,
frame_id_[base_stream_]);
} else {
publishStaticTF(ros::Time::now(), zero_trans, zero_rot, camera_link_frame_id_,
frame_id_[base_stream_]);
}
Identify FEMTO series cameras by PID (FEMTO_BOLT, FEMTO_MEGA).
For FEMTO series, additionally compute the transform from depth to color sensor to ensure proper mapping across models.